File:T1.png
T1.png (726 × 303 pixels, file size: 48 KB, MIME type: image/png)
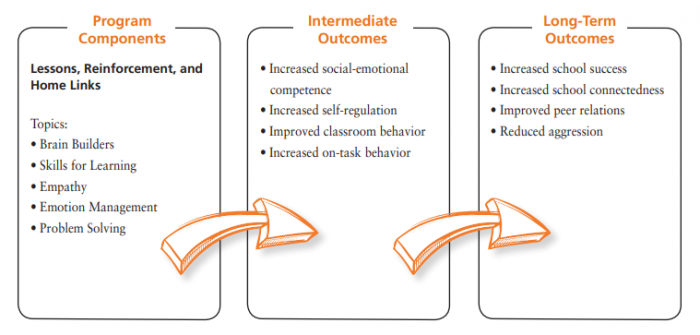
Logic Model
Review of research
|
Skills for Learning
|
Empathy
|
Emotion Management
|
Problem Solving
|
|
🔎 See more: Full Review of research
The following illustrates how the evidence-based CLISE program elements align with CASEL’s core social-emotional learning (SEL) competencies. Note the considerable overlap across CASEL’s core SEL competencies. This reflects how self-regulation and social-emotional skills are built across the primary CLISE curriculum.
What Is CASEL?
Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) is the nation’s leading organization advancing the development of academic, social, and emotional competence for all students. Their mission is to help make evidence-based social-emotional learning an integral part of education from preschool through high school. To that end, CASEL has identified five interrelated SEL core competencies: self-management, self-awareness, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making.
How does the CLISE program develop Core SEL Competencies?
| Program Element | Key Skill(s) Developed | CASEL Core SEL
Competencies |
|---|---|---|
| Brain Builder Games (1–3) | Executive-function skills | Self-Management |
| Skills for Learning | • Focus attention
• Listen with attention • Identify and use self-talk • Be assertive • Remember directions • Stay on task • Ignore distractions |
• Self-Management
• Self-Awareness |
| Empathy | • Identify and understand one’s own and others’ feelings
• Build vocabulary of feelings words • Begin to take others’ perspectives • Listen to others • Have empathy • Show compassion |
• Relationship Skills
• Responsible Decision-Making • Self-Awareness • Social Awareness |
| Emotion Management | • Identify and understand one’s own feelings
• Recognize strong feelings • Calm down strong feelings • Use the Ways to Calm Down |
• Responsible Decision-Making
• Self-Awareness • Self-Management |
| Problem Solving | • Friendship skills
• Calm down before solving problems • Describe the problem • Think of many solutions • Explore the consequences of the solutions • Pick the best solution |
• Relationship Skills
• Responsible Decision-Making • Social Awareness |
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:34, 27 February 2023 |  | 726 × 303 (48 KB) | Admin (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: